Pipeline Hazard
Structural Hazard
Conflict for use of a resource
Solution
- Stall
- Resource Duplication
Example
- Load/Store requires data access.
- Instruction Fetch would have to stall
- Cause pipeline bubble
- Solution:
- Separate Instruction/Data Memory
- Multiple Read Ports
Data Hazard
An instruction depends on completion of data access by a previous instruction
Example: Read-After-Write (RAW)
Reading value from register before previous instruction writes the result
Solution
- Freezing (Stall)
- Data Forwarding
- Compiler Scheduling Optimization
- Out-of-order Execution
How to Stall
- Prevent Update of PC
- Force control values in ID/EX register (stores result) to 0 => MEM/WB do nop
Data Forwarding
Value가 write되기를 기다리지 말고 각 hardware unit에서 연산 결과를 바로 forwarding해서 사용
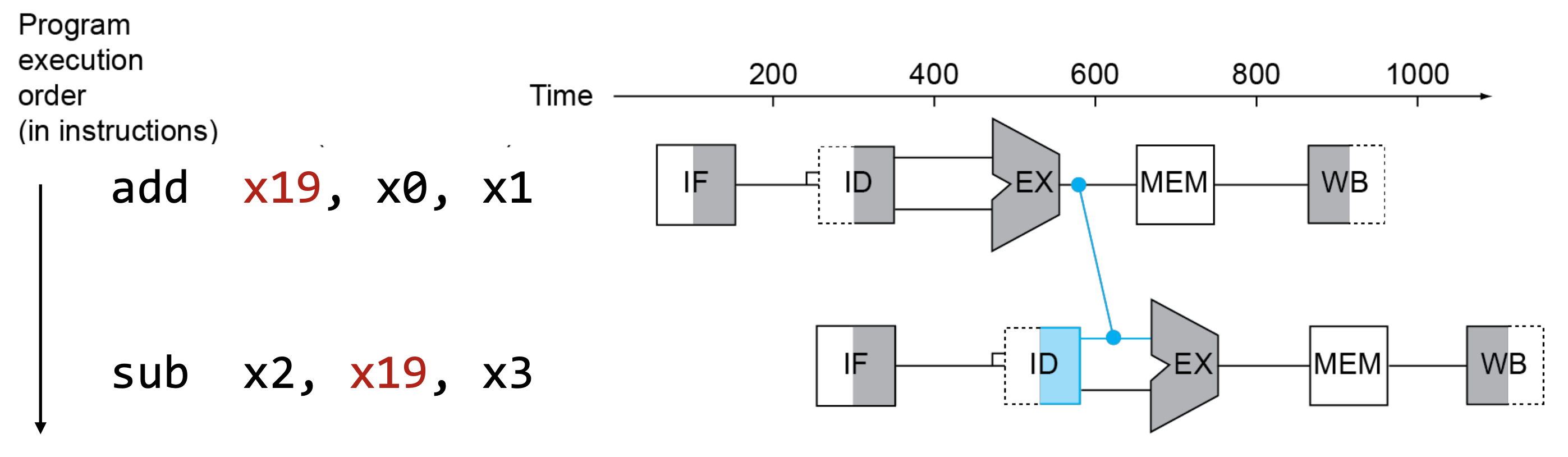
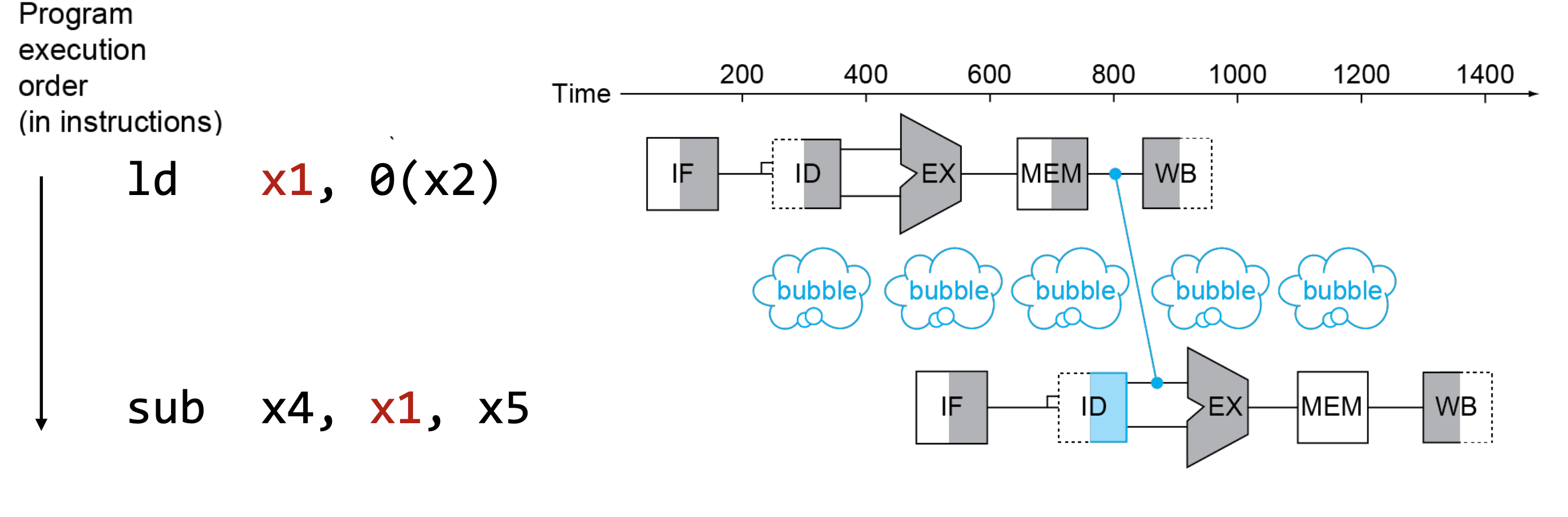
Load-Use Data Hazard
이전 instruction이 Load인 경우 execution stage에서 계산 되는 것이 아니라, 그 다음 stage인 memory stage에서 value를 가져오기 때문에, forwarding을 한다고 해도 stall을 피할 수 없다.
Compiler Scheduling Optimization
Reorder code to avoid use of load result in the next instruction
Control hazard
Branch instruction에서 next instruction이 달라질 수 있음
Solution
- Stall
- Branch Prediction
- Compiler Scheduling Optimization
Branch Prediction
Predict next branch. If wrong, cancel (flush the pipeline).
Branch Prediction Buffer
Buffer the prediction result. Update the prediction on actual result.
- 1-bit => Double miss on nested loop
- 2-bit prediction => (Strong/Weak) (Taken/Not-Taken)
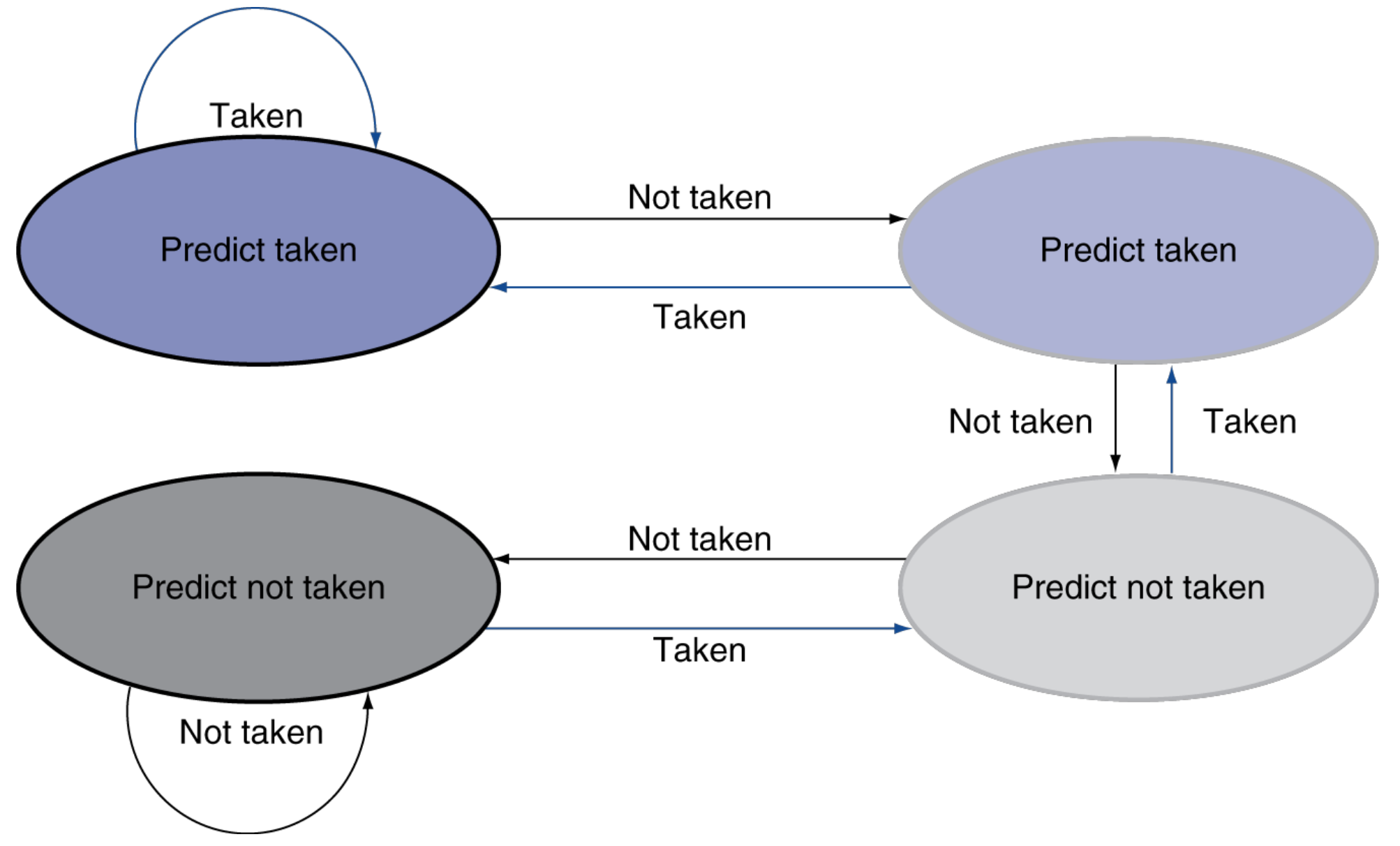
Branch Target Buffer
Even with predictor, still needs to calculate target. Buffer the target address => indexed by PC
