Address Translation
MMU가 virtual address를 physical address로 변환하는 과정.
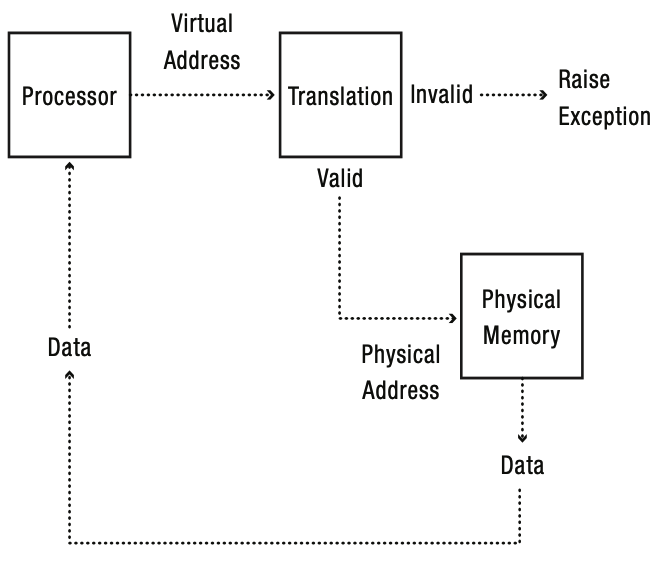
Address translation은 다음과 같은 목표를 가진다.
- Protection - memory에 대한 invalid access를 막아야 한다.
- Sharing - process간 memory를 공유할 수 있어야 한다.
- Sparsity - address space의 sparse한 특성을 잘 활용한다.
- Efficiency - resource overhead 및 waste를 줄이고, translation을 효율적으로 한다.
Contiguous Allocation
각 process에 memory resource를 할당할 때 contiguous allocation은 여러 문제를 가진다.
Dynamic Memory Size
Address Space를 전부 할당하는 것은 엄청난 resource 낭비이다. 그렇다고 실사용량만큼 할당하려고 하니 동적인게 문제다.
- 너무 조금 할당하면 메모리 사용량 증가에 따른 잦은 reallocation이 발생
- 너무 많이 할당하면 메모리 낭비
Free Management
각 memory slot이 사용중인지 알기 위해 발생하는 metadata의 크기가 너무 크다 (1byte당 1bit)
Fragmentation
각 process에 physical memory를 할당할 때 contiguous allocation은 fragmentation을 발생시킨다.
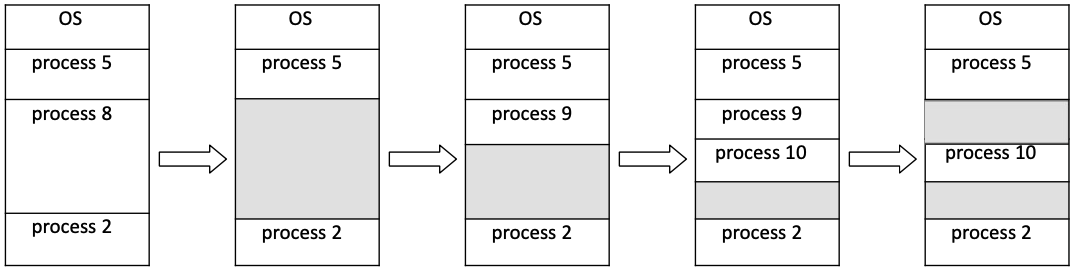
Segmentation
Segment is a contiguous region of virtual memory, which can be located anywhere in physical memory.
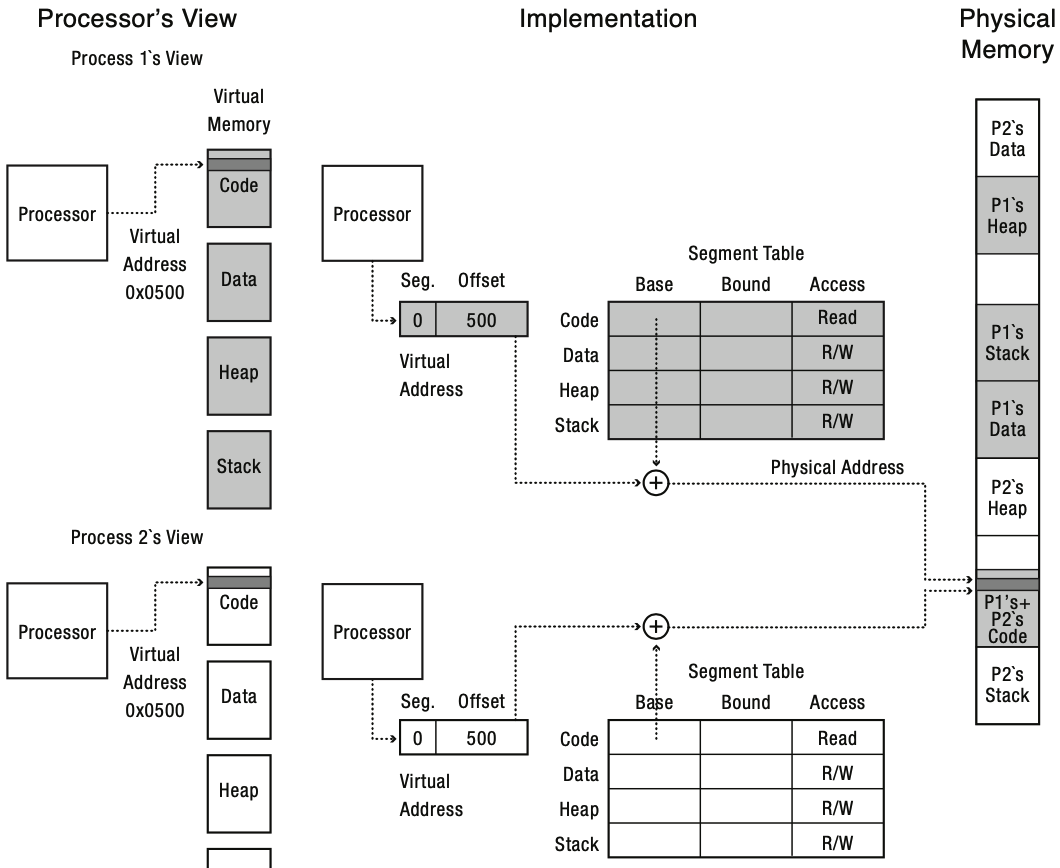
- Virtual Address = [segment-number, offset]
- Segment Table = (start address, length, access permission)
그러나 segmentation 방법도 fragmentation에서 자유로울 순 없다. 왜냐하면 결국 segment의 길이가 동적이기 때문이다.
Copy On Write
Process를 fork할 때 virtual address가 동일한 memory region을 가리키도록 하고, segment에 write할 때 copy하는 방법.
Paging
Segment 대신 page라는 고정 길이 단위로 메모리를 분할하여, page 단위로 메모리를 관리. 참고로 physical page는 frame이라고도 부른다.
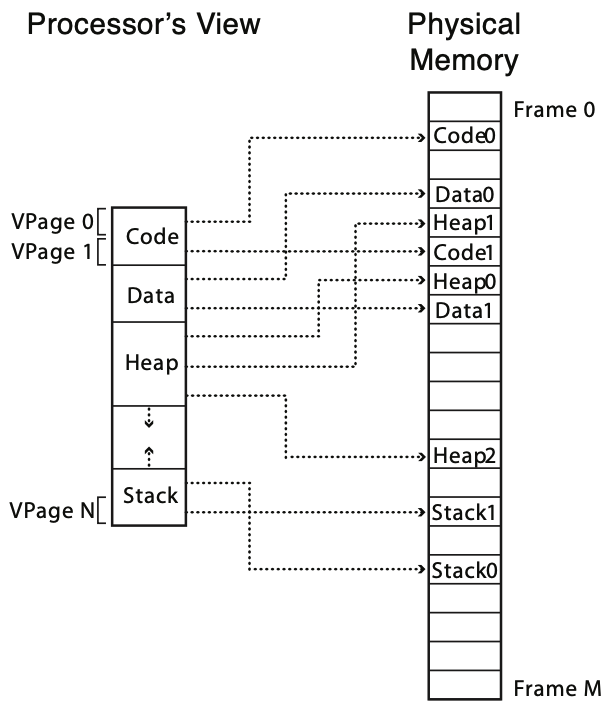
즉, 고정 길이 단위를 사용함으로서 fine-grained management로 fragementation을 없애고, 실사용량만큼 메모리를 할당하여 효율을 높이는 방법이다. 뿐만 아니라 free page를 tracking할 때 byte당 1bit가 아니라 page당 1bit라 overhead가 적다.
